During the global COVID-19 pandemic, numerous measures were taken to mitigate the spread of infection. Among these was the closure of childcare centers since non-pharmaceutical interventions like social distancing or mask-wearing are not applicable to preschool children. However, this has led to extensive negative effects, such as reducing educational, psychosocial, and nutritional opportunities for children and increasing the risk of parenting-related exhaustion, which poses a risk factor for child abuse. The World Health Organization addressed violence against children as “a hidden crisis of the COVID-19 pandemic”. Therefore, it is essential to research testing and quarantine strategies that allow the reopening of childcare facilities, while simultaneously preventing infection spread.
KITE (KIndergarten Test scenario Evaluator) is a state-based model for simulating the spread of different airborne viruses in kindergartens. The current main focus lies on COVID-19.
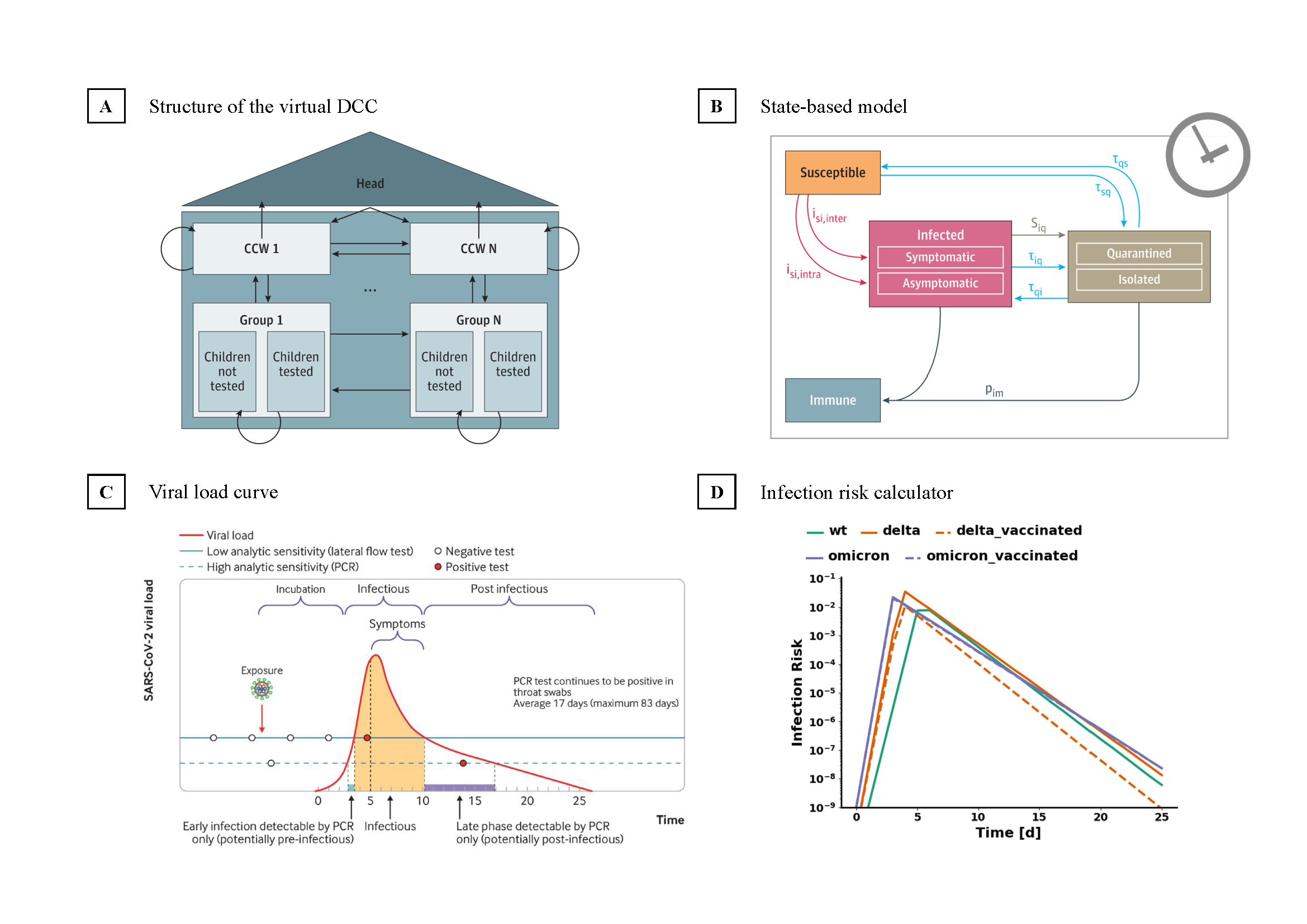
We developed a state-based model for simulating the spread of airborne viruses e.g. COVID- 19 in child care facilities. This framework allows monitoring the viral spread for various scenarios, such as different quarantine policies, the percentage of children participating in regular testing, different testing modalities (PCR-Test, rapid antigen tests, pool tests), the test frequency, or even certain test days. Moreover, mask wearing or vaccination of individuals are used to reduce the infection spread further.
Experimental Collaborators
- Institute for Hygiene and Microbiology in Würzburg, Germany
- University Children’s Hospital in Würzburg, Germany