In this study we analyze the the immune evasive pathogen C. albicans. The secreted pH regulated antigen 1 (Pra1) is a protease and cleaves C3, the key molecule for cell opsonization. The paradox of this mechanism is that this cleavage of C3 produces a molecule that is very similar to the opsonin C3b. At a first glance it is not obvious why this protease has a regulatory influence on the system. This paradox is to be deciphered with a mathematical model.
Experimental Collaborators
- Infection biology group at the Leibniz-HKI in Jena, Germany
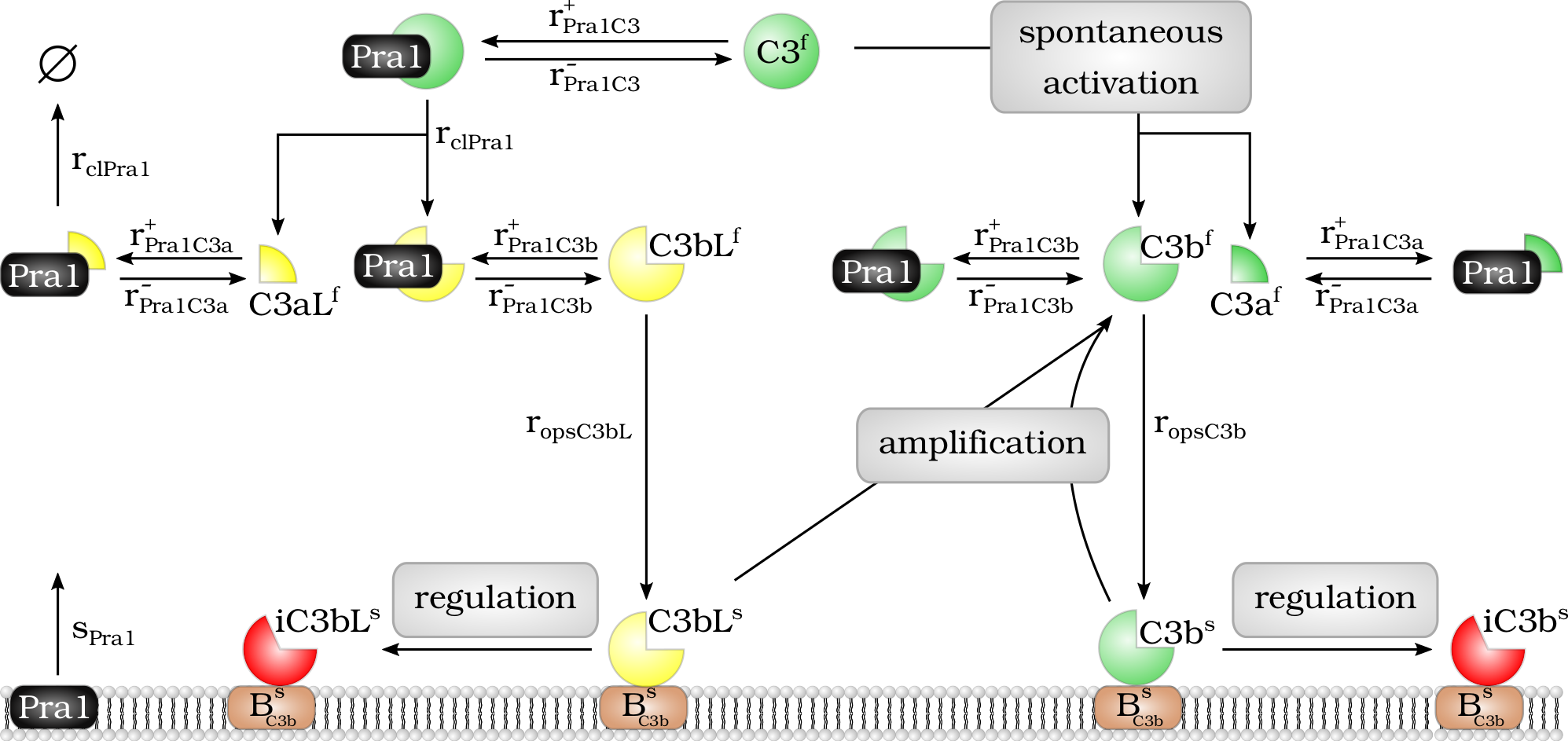
Model of the Pra1 interaction with the complement molecule C3 and its cleavage products.
Model of the $Pra1$ interaction with the complement molecule $C_3$ and its cleavage products. Fluid phase $Pra1^f$ binds to $C_3^f$ and cleaves it into fragments $C_3aL^f$ and $C_3bL^f$. In addition, $Pra1^f$ binds to the cleavage products $C_3a^f$, $C_3b^f$, $C_3aL^f$ and $C_3bL^f$ and blocks their effector function. The molecule $C_3bL^f$ can bind to the cell surface like $C_3b^f$ and there enhance complement activation via the $C_3$-convertase of the alternative pathway or it is inactivated by regulators and cleaved to $iC_3bL^s$.
For this purpose, the existing DynaCoSys model is extended to include the dynamics of Pra1 and its cleavage products. The deviation of opsonization on the surface and of the molecules in the fluid around the cell will be analyzed in comparison to a cell without Pra1 secretion.